简介
线程池其实就是为了减少线程的频繁创建和销毁,从而能够使线程得到充分利用,这样就可以提高系统的性能和运行效率。
常见的线程池创建方式
- ThreadPoolExecutor
- 使用Executors来创建各种线程池,比如newFixedThreadPool(int threadNum);
线程池execute运行策略
其实execute和submit执行逻辑都一样,submit底层实现其实也是在execute方法的基础上来进行实现的。
那我们来看下execute的源代码吧java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor#execute。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
其中涉及到work的流程,有个博客写的不错,可以参考一下:
1
https://juejin.cn/post/6866054685044768782
详细解释
- 当任务数小于coreNum的时候,创建一个线程来执行任务。
- 当任务数量大于coreNum的时候,并且小于队列规定最大任务数量的时候,把任务放到队列里面
- 当任务数大于coreNum的时候,并且线程数还没有达到最大线程数的时候,创建最大线程数量来执行任务
- 大于最大线程数,队列已满,调用拒绝策略
其实所有的任务都是先进入到任务队列里面,然后再从队列里面取出来,给线程再执行。
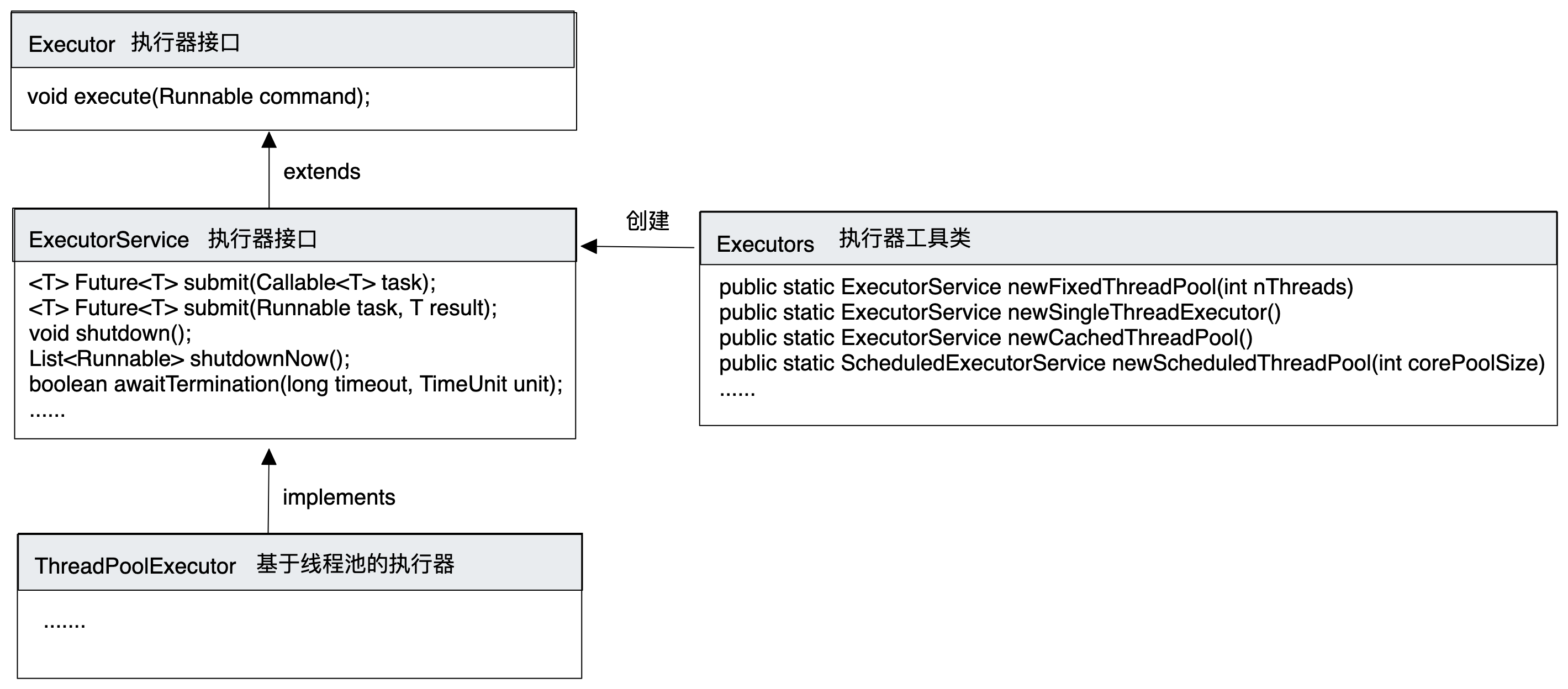
Executor、ExecutorService、Executors直接的关系
Executor和ExecutorService是执行器接口;Executors可以看做是一个线程执行器的工具类。