迭代器简介
迭代器其实通俗的来讲就是遍历(loop)容器的一些过程,场景的迭代方式有 for循环、for-each循环、迭代器、forEach()函数。
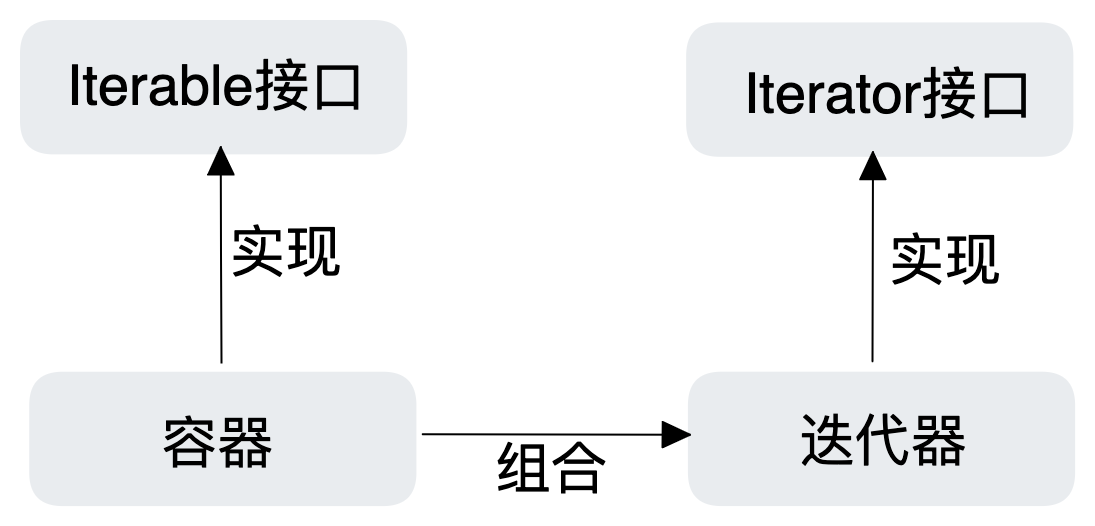
Iterable和Iterator区别
其实根据名称也能够探寻一二,就拿Iterator来说把,一看带是以or结尾的,那么就这个这个接口肯定就是执行迭代执行人嘛。转换成专业术语来说,可以这么来理解:
Iterable这个接口负责定义生成Iterator,而Iterator这个接口则负责定义迭代都有哪些操作步骤比如hasNext,next,remove这些操作。
为什么普通的迭代在删除的时候会出现一些问题?
常见的有两种问题
- 删除数据不彻底,也就是说没有把符合条件的数据都给删除掉。
- 删除的时候报错了;比如如下代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
//这里我们就拿ArrayList来进行举例
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("1");
list.add("1");
list.add("1");
list.add("1");
for (String s : list) {
if (s.equals("1")){
list.remove(s);
}
}
这是因为ArrayList底层就是以数组来进行存储的,当删除一个元素的时候,这个数组的数据会发生移动,所以产生了上面的两种场景错误。
为什么使用迭代器就没有这个问题呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
// 游标(下一个元素的位置)
int cursor; // index of next element to return
// 当前的位置
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// ....
}
以上就是Iterator的源码,看源码就知道了。有几个要点
- ArrayList.this.elementData 是一个缓存数组;
- cursor 是一个游标,会存储下一次访问的下标的值;
- lastRet保存的是当前返回的下标值